Heavy equipment for use at the job site continues to become more efficient. Dramatic improvements have been made on various specific machinery and continues to be made at a rapid rate. This evolution is propelled now by a few key industries busy changing the game. Here are 5 leading-edge developments in the construction industry:
1. 3D Printing
China-based 3D printing construction company WinSun “expects 3D printing will save construction companies up to 50 percent on the cost” of building a house. This could prove to be a lifesaver for construction managers with access to this technology and could lead to increased competition within the construction field. Competition means lower prices for consumers, which could mean a shift from a rental to an ownership mindset.
What’s Next for 3D Printing?
Among those calling for construction professionals to take advantage of the potential of 3D printing is University of Southern California professor Behrokh Khoshnevis, creator of Contour Crafting. In a Ted Talk he gave in 2012, he said, “If you look around yourself, pretty much everything is made automatically today—your shoes, your clothes, home appliances, your car….The only thing that is still built by hand are these buildings.” And later: “Construction, as we know it today, is wasteful, costly, and often over budget.”
3D printing will most likely not solve the construction industry’s skilled worker shortage, recruit up and coming talent, or remove human error in planning construction projects. It seems clear that 3D printing presents promising opportunities for the construction industry to become both greener and more cost-effective, often by considerable margins. As 3D printing research continues to develop, it will be exciting to see the benefits the technology will have on the many facets of the construction industry.
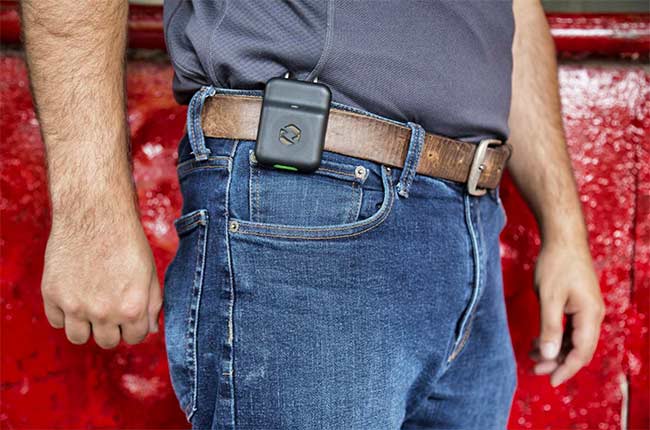
2. Wearable Technology
Here are 4 advantages illustrating how wearable technologies are helping to shape the construction industry:
-
Improved Safety
One of the biggest benefits of wearable technology in construction is the safety improvements. Wearable devices are typically worn on a worker’s waist belt, allowing for constant connection with site supervisors. If an accident occurs, wearable technologies can help to save lives through slip and fall detection. Through GPS technology, it can alert supervisors and give them a worker’s exact location. Injuries can be extremely time-sensitive, highlighting the importance of responding and acting as quickly as possible.
-
Streamlined data collection process
Manual headcounts and safety checks are prone to error and extremely time-consuming. Wearable technology streamlines the process,, giving you a more accurate and thorough set of data. Instant data collection also allows the manager or supervisor to spend their time working on other areas that need their attention. This results in more efficient project management and enhanced safety on the job site!
-
Attractive to millennials
It’s no secret that the construction industry’s skilled workforce is slowly dwindling. To make matters worse, there isn’t a huge influx of incoming workers. This is especially true when it comes to millennials. The best way to fix this problem? Technology! Young professionals have grown up with technology and want to see it being used in their workplace. If the construction industry wants to attract talented young workers, wearable technology is a great place to start. By implementing the latest forms of technology the construction industry can show the world that they are as innovative as every other industry!
-
Enhanced communication
Wearable technology gives workers the ability to communicate in real-time. Gone are the days of chasing down other workers or playing phone tag! Wearable technology keeps you connected to your team members at all times and ensures that everyone is kept in the loop.
3. Augmented Reality
Accuracy is always important in any project to avoid wasting money and time due to any adjustments later. Before the project is executed, AR provides teams with a walkthrough of the entire project – including its details and exact measurements.

Augmented reality can display accurate images with the entire space’s recreation. And with that, planning becomes more efficient and saves the time and effort of the team because they do not need to build different design plans but just view their options through augmented reality. Project members, thus, can ensure greater accuracy with virtual models.
Effective collaboration, including communicating ideas and creativity in the form of design, is also made easy! Architects and designers can present their creative ideas or turn client visions into models with AR.
4. Robotics
One of the uses of robotics is to allow for greater automation in various processes. In many aspects of construction, specifically manufacturing, packing and building, automating these processes is becoming the goal. With greater development in robotics and machinery, construction companies are becoming more open to utilizing technology.

With robotic technology, you can expect traditional construction activities like welding, material handling, packing, dispensing, cutting and packing to be fully automated. This will not only allow for precision and accuracy throughout all construction processes, it represents a significant time and financial savings as well.
5. Predictive Analytics
-
Design:
Big data, including building design and modeling itself, environmental data, stakeholder input, and social media discussions, can be used to determine not only what to build, but also where to build it. Brown University in Rhode Island, US, used big data analysis to decide where to build its new engineering facility for optimal student and university benefit. Historical big data can be analyzed to pick out patterns and probabilities of construction risks to steer new projects towards success and away from pitfalls.
-
Build:
Big data from weather, traffic, and community and business activity can be analyzed to determine optimal phasing of construction activities. Sensor input from machines used on sites to show active and idle time can be processed to draw conclusions about the best mix of buying and leasing such equipment, and how to use fuel most efficiently to lower costs and ecological impact. Geo-location of equipment also allows logistics to be improved, spare parts to be made available when needed, and downtime to be avoided.
The variety of inputs in big data allows better levels of certainty about status reports and forecasts. The analytics can provide more helpful indications of risk levels before a threshold is exceeded and an alert generated. They also offer insights that traditional systems simply cannot.






Leave A Comment